This Is How To Overcome The Curve Of Forgetting Today!
I Have A Challenge For You
I want you to memorise these nonsense three letter words right now:
HEQ YIN GES DAX BOK
Now go read the rest of this article and recall these words at the end of the article.
Are you ready?
3, 2, 1 GO!
Why?
In 1885, Hermann Ebbinghaus performed this exact same experiment on himself, memorising lists of meaningless syllables in the form consonant, vowel, consonant. After memorising the list he tested himself periodically to figure out how many of these nonsense words he remembered at various points of time. In short, he found out that his memory of these words had rapidly decayed, discovering the basic processes of learning and forgetting. This was his most significant discovery, the curve of forgetting.
You might be familiar with this theory already.
Have you ever cram studied for an exam the night before and forgotten everything the next day?

Hermann Ebbinghaus Memory Theory
The Hermann Ebbinghaus memory theory, a discovery which is over 100 years old, is a mathematical formula which describes the rate at which we forget information after initially learning it.
The discovery is defined by the equation: R = e^(-t/s)
Where:
R = how readily you can recall something
s = the strength of your memory
t = the amount of time that has passed
e = Euler’s number
This makes more sense in graph form.
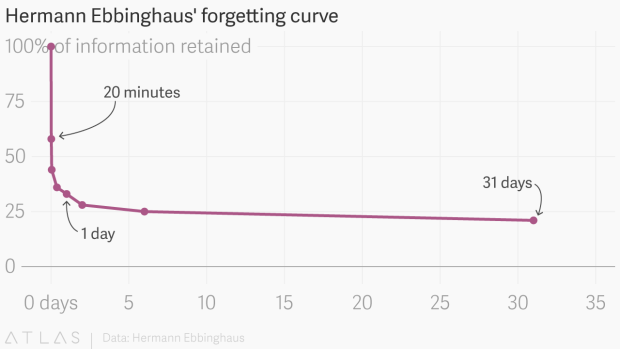
The bad news is, the gradient, representing how much you remember, is steeper than what you would think.
As you can see in this graph, the initial gradient is straight down, representing how much information you have forgotten in the first 10 to 20 minutes after learning new information. The gradient then levels off, meaning that any information that you did retain will stick with you for many days afterwards.
How To Retain More Information
To make the gradient of R more gradual it is vital to repeat and review information at certain intervals over time to increase the strength of your memory. There needs to be space between repetitions. You can’t just revise new vocabulary or a new fact 20 times in one hour and then overcome the curve.
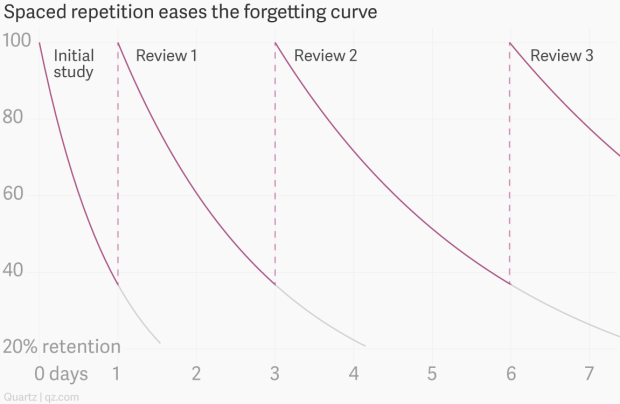
As you can see in this graph, by reviewing the information every few days, the percentage of retention goes back up to 100%.
To improve your memory and ultimately forget less you need to constantly be revising new and old topics. But this does not mean you go back and find your old work and start looking at it everyday. Some things obviously need more revision than other things and this can be difficult to keep track of.
But with so much information being expected of you to learn at school or university it can become difficult to remember what content to revise and when to revise the content. This is why I have created a printable to help you overcome the curve of forgetting.
To use the theory of spaced repetition with your studies, I suggest recording a sub-topic with it’s date and revising it an hour after learning it, a day after learning it, a week after learning it, two weeks after learning it, a month after learning it, 3 months after learning it and 6 months after learning it.
If you use a curve of forgetting printable it becomes easier to track what needs to be studied and what doesn’t and it follows these time intervals that are supported by spaced repetition research.
Curve Of Forgetting Printable Sheets
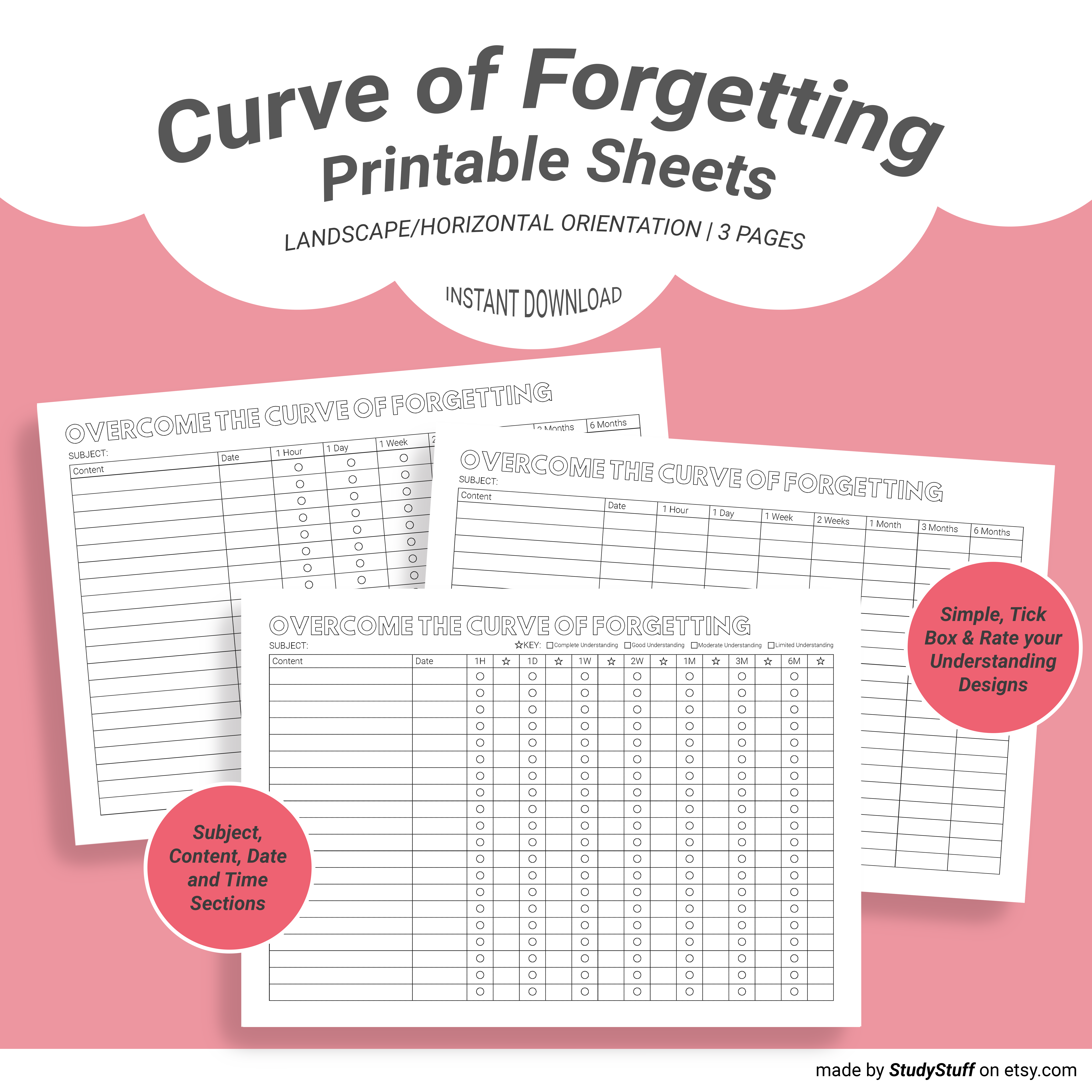
Use This Planner To:
- Overcome the curve of forgetting
- Effectively revise class content with spaced repetition
How To Use:
In the content column write down a specific topic that you just learnt with the date in the column next to it. The following columns tell you when you need to revise this topic based off scientific research into optimal revision intervals. These are 1 hour, 1 day, 1 week, 2 weeks, 1 month, 3 months and 6 months in this printable. This printable has 3 different designs. In the ‘simple design’ you can write down the date for the next revision time slot in the columns. In the ‘tick box design’ you can check off each time you review a topic under each recommended time interval and finally in the ‘rate your understanding design’ you can you can check off revisions and colour in the box according to the key to rate your understanding to help you prioritise which sub-topic you need to study first. You can look at the product images for examples ☺
What’s Included:
1 PDF With 3 Pages
- Simple Design
- Tick Box Design
- Rate Your Understanding Design
You Can Get It Here
Alternative Methods To Overcome The Curve Of Forgetting
The Overcome The Curve Of Forgetting Printable is fantastic for larger chunks of information that need to be revised but not single facts for example. So an alternative method for more specific fact based spaced repetition learning is to use flashcards. These can either be digital or physical cards.
Digital flashcards that utilise spaced repetition, for example StudiesApp, Anki, QuizletPlus etc., are good for people who like phone reminders and notifications to study. These apps are also very good for studying while taking public transport.
But if you are more a pen and paper person, you can make your own flashcards and apply the theory of spaced repetition. Simply make the cards and some boxes to put them in that represent the different space intervals. Study each card and move them up the boxes accordingly.
I have a printable study box set which can help you get started with physical flashcards and spaced repetition.
Do You Remember The 5 Words I Got You To Memorise At The Beginning Of The Article?
HEQ YIN GES DAX BOK
Maybe you can use the theory of spaced repetition to help yourself overcome the forgetting curve.
If you take notes using your iPad, you need to know these 12 iPad note taking tips! They will make …
There are many different note taking methods that can work well for language learning. To take effective notes for language …
To take pretty notes you need to firstly choose a consistent colour scheme. Next you should draw an eye catching …
To take notes on a PDF on an iPad you need to use a note taking or PDF reading app …
To get motivated to do school work one should set SMART goals, work in a motivating environment, break large projects …
To take aesthetic notes one needs to choose a consistent colour scheme, use eye catching titles and headers, invest in …






